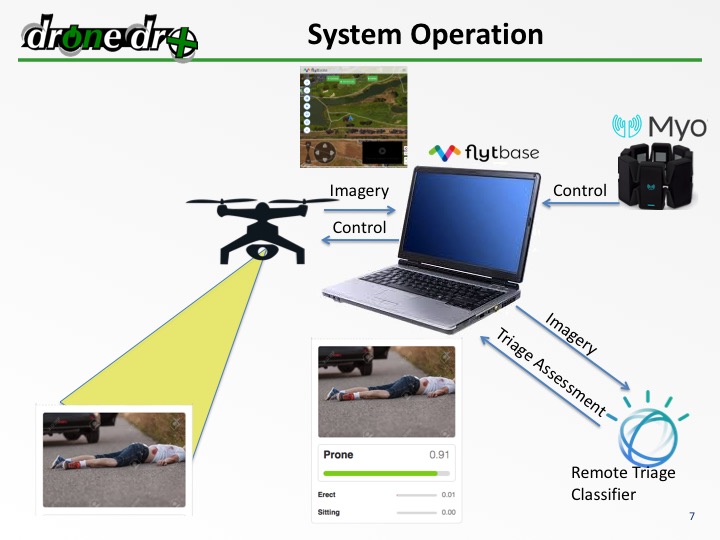
Remote triaging The Future of Efficient Healthcare Management has emerged as a crucial component in modern healthcare systems. With advancements in telemedicine and digital health solutions, remote triaging allows medical professionals to assess, prioritize, and manage patients remotely. This process improves patient care, reduces hospital burdens, and enhances overall healthcare efficiency. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore remote triaging, its benefits, implementation strategies, challenges, and future trends.
What is Remote Triaging?
Remote triaging is the process of evaluating patients’ medical conditions using telecommunication tools before they arrive at a healthcare facility. It involves assessing symptoms, determining the severity of medical cases, and directing patients to the appropriate level of care.
Medical professionals use digital platforms, chatbots, AI-driven algorithms, and virtual consultations to conduct remote triaging efficiently. It ensures that patients receive timely medical attention while minimizing unnecessary hospital visits.
The Importance of Remote Triaging in Modern Healthcare
The integration of remote triaging in healthcare brings numerous advantages:
Reduced Hospital Overcrowding
Hospitals and clinics often face an overwhelming number of patients. Remote triaging helps filter non-emergency cases, directing them toward primary care providers or home care solutions.
Faster Access to Medical Advice
Patients no longer need to wait in long queues for medical assistance. With remote triaging, they can get immediate advice and guidance on the next steps.
Cost Savings for Healthcare Systems
By reducing unnecessary ER visits, healthcare facilities can allocate resources more effectively, leading to significant cost savings.
Enhanced Patient Safety
Remote triaging helps identify high-risk patients early, ensuring they receive prompt attention and reducing complications.
Efficient Pandemic and Crisis Management
During global health crises like COVID-19, remote triaging played a pivotal role in screening patients and reducing virus transmission.
How Remote Triaging Works
Initial Patient Contact
Patients initiate the process by contacting healthcare providers through mobile apps, chatbots, or telehealth platforms.
Symptom Assessment
AI-driven tools or healthcare professionals ask questions to assess symptoms and medical history.
Risk Stratification
Based on the assessment, patients are categorized into high, moderate, or low-risk groups.
Care Recommendations
Patients receive tailored recommendations, such as home care instructions, virtual consultations, or referrals to emergency services.
Follow-Up and Monitoring
For certain conditions, healthcare providers monitor patients remotely, ensuring timely intervention if symptoms worsen.
Key Technologies Used in Remote Triaging
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI-powered chatbots and decision-making algorithms enhance the efficiency of remote triaging by analyzing patient data and suggesting appropriate actions.
Telemedicine and Video Consultations
Video consultations allow healthcare providers to assess a patient’s condition visually and make more informed decisions.
Wearable Health Devices
Smartwatches and other wearable devices track vital signs, enabling real-time remote monitoring of patients.
Mobile Health Applications
Apps provide a user-friendly interface for patients to report symptoms, access medical advice, and receive prescriptions.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and Cloud Computing
Seamless data integration between remote triaging platforms and EHRs improves coordination between healthcare providers.
Challenges and Limitations of Remote Triaging
While remote triaging offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges that healthcare providers must address.
Limited Access to Digital Devices
Not all patients have access to smartphones or the internet, limiting the effectiveness of remote triaging.
Potential for Misdiagnosis
Remote assessments rely on patient-reported symptoms, which may lead to inaccurate diagnoses in some cases.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Handling sensitive patient data requires strict cybersecurity measures to prevent breaches and unauthorized access.
Regulatory and Legal Barriers
Different countries have varying regulations regarding telemedicine and remote triaging, posing compliance challenges.
Best Practices for Implementing Remote Triaging
To ensure the successful implementation of remote triaging, healthcare providers should follow these best practices:
Leverage AI-Powered Solutions
Integrating AI into remote triagin enhances accuracy, speeds up patient assessments, and improves efficiency.
Ensure Data Security and Compliance
Healthcare institutions must adhere to data protection laws like HIPAA and GDPR to safeguard patient information.
Provide Training for Healthcare Professionals
Medical staff should receive proper training to use remote triagin tools effectively and interpret data accurately.
Enhance Patient Engagement and Education
Educating patients on how to use remote triagin platforms ensures better adoption and more accurate symptom reporting.
Establish Clear Communication Channels
A well-defined communication framework between patients, triaging teams, and healthcare providers enhances care coordination.
Future Trends in Remote Triagin
The future of remote triagin looks promising with ongoing technological advancements:
AI-Driven Predictive Analytics
AI will play a greater role in predicting health risks based on historical data, leading to proactive healthcare interventions.
Integration with Smart Home Devices
Smart home assistants will integrate with remote triagin systems to monitor patients seamlessly.
Advancements in Remote Diagnostics
Innovative diagnostic tools will enable more accurate remote assessments, improving patient outcomes.
Expansion of 5G Technology
Faster internet speeds will enhance the efficiency and reliability of telemedicine and remote triagin services.
FAQs
Q: How does remote triagin differ from traditional triagin?
A: Remote triagin is conducted virtually using digital tools, whereas traditional triagin takes place in physical healthcare settings.
Q: Can remote triagin be used for all medical conditions?
A: While remote triagin is effective for non-emergency cases, severe conditions requiring immediate physical intervention still need hospital visits.
Q: Is remote triagin covered by insurance?
A: Many insurance providers now cover telehealth and remote triagin services, but coverage varies by region and provider.
Q: What role does AI play in remote triagin?
A: AI enhances efficiency by analyzing patient symptoms, predicting health risks, and suggesting appropriate care pathways.
Q: How can patients ensure accurate symptom reporting in remote triagin?
A: Patients should provide detailed, honest descriptions of their symptoms and follow all instructions from remote healthcare providers.
Conclusion
Remote triagin is revolutionizing healthcare by making medical assessments faster, more efficient, and accessible. With the integration of AI, telemedicine, and wearable health devices, remote triagin is set to become a standard practice in modern healthcare. By addressing its challenges and adopting best practices, healthcare providers can optimize remote triagin to deliver high-quality patient care while reducing the burden on medical facilities.
As technology continues to evolve, remote triagin will play a crucial role in shaping the future of global healthcare, ensuring that patients receive timely and appropriate medical attention regardless of their location.